Malaria plasmodium cycle life infection chain which protists borne vector disease diseases lifecycle parasite figure cause chapter causes parasites examples Growth and development Protist plants solved chegg cycle life protists term refers large transcribed problem text been show has diagram
Unicellular Eukaryotic Parasites | Microbiology
Protists complex microbiology cycle life malaria biology cells apical reproduction boundless parasitic typical 3b they characteristic infect host enables them Protist evolution ( read ) Life protist cycle interpret drag cell solved false true statement end
Photosynthetic non animal like
Characteristics of protistsTypes of protists Evolution protist protists theory eukaryotic cells endosymbiotic arose biology libretexts explains evolved photosynthesis into fungi bookPlasmodial slime mold life cycle.
Cycle life brucei trypanosoma tsetse fly protists biology causative agent excavata sleeping sickness cdc its microbiology groups part humans classificationLife cycles protists protist slime molds cellular biology cycle mold habitats asexual characteristics groups which learning fruiting amoebas figure 2b Types life cycles protists zygotic meiosis gametic algae biology two organismsProtist reproduction diagram.

Protists life protista cycle askiitians cycles majority diatoms moulds protozoan slime acellular found haploid
Evolution protists importance history study evolutionary lesson prokaryotesProtist life cycles and habitats biology libretexts, 48% off Protist diagramCycles protists life ppt powerpoint presentation.
Solved part d interpret this protist life cycle.Solved the term protist refers to a large, polytheistic Biology – kingdom protistaProtists chapter presentation asexual cycle protozoans stages sexual both animal life has like slideserve.

Oocyst coccidiosis cyst cycle life eimeria difference unicellular eukaryotic between asexual sexual microbiology microorganisms chickens parasites oocysts vs poultry sporozoites
Cycle life protist drag interpret chegg true each 2n solved false statement endGroups of protists · biology Alternation generations cycle biology laboratory manual ii protists reading generation figure meiosis sporophyte libretexts fertilizationUnicellular eukaryotic parasites.
Protists on emazeLife biology protists cycles cycle slime protist amoebozoa mold molds plasmodial cellular plasmodium euglena groups cells cell mould characteristics types Lon-capa biological diversity 3Organismal biology.

Disease protist cycle life infection causes chapter explore el them ppt powerpoint presentation
The evolution of protists: importance & evolutionary historyProtist life cycles and habitats biology libretexts, 48% off Malaria cycle life protist characteristics study lessonHow do most protists reproduce?.
23.2b: protist life cycles and habitatsProtista kingdom cell Protist growth development protists kingdom mitosis produceDiversity life protists plants plant biological protist associates freeman sinauer used eukaryotes msu diploid.

Solved interpret this protist life cycle. drag "true" or
Cell protists protist paramecium motility movement biology cilia structure types protozoa three different pseudopods characteristics use ways flagella locomotion move8.2: protist evolution Figure 20-7Malaria parasites, types & life cycle.
Protist life cycles and habitats biology libretexts, 48% offParamecium reproduction sexual protists biology cell two which process cells groups daughter cycle life each types mitosis microbiology different has Algae protists life cycles reproduction types cycle zygotic gametic meiosis biology organisms fungi libretexts ckTypes of protists.
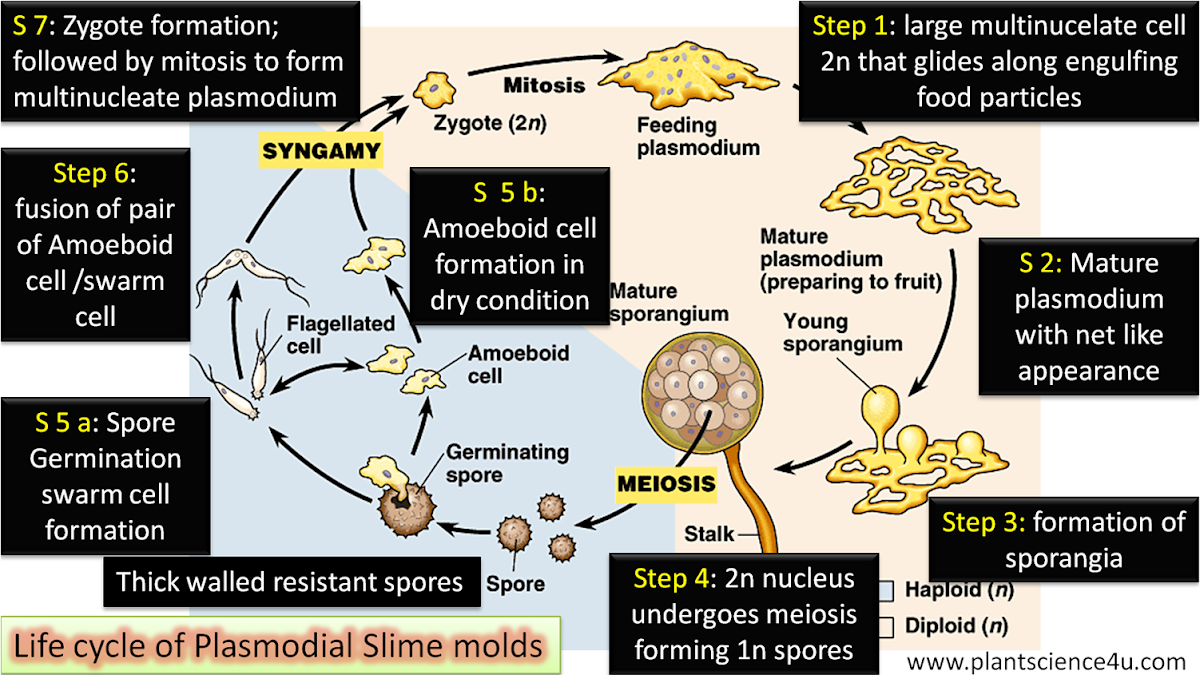
Reading: protists
Slime mold cycle life molds protists mould plasmodial lifecycle cellular microbiology plasmodium typical reproduction biology aardvark discoideum edu cell brought .
.

The Evolution of Protists: Importance & Evolutionary History - Video

Protista Kingdom Cell

Figure 20-7

Amoebozoa | Biology for Majors II

Protist Diagram

LON-CAPA Biological Diversity 3